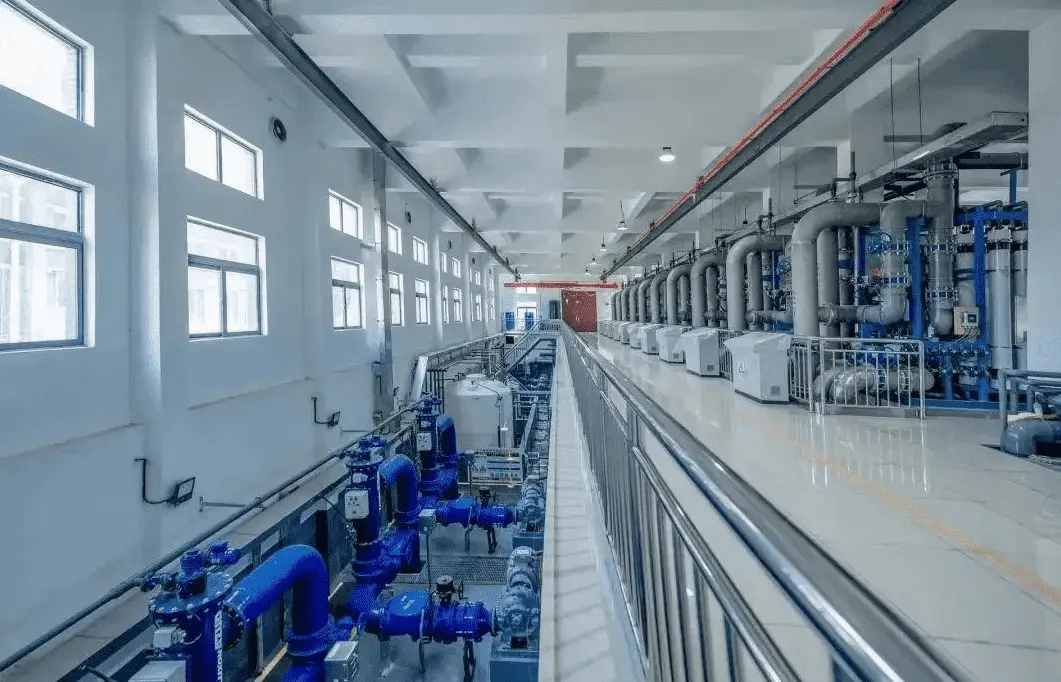
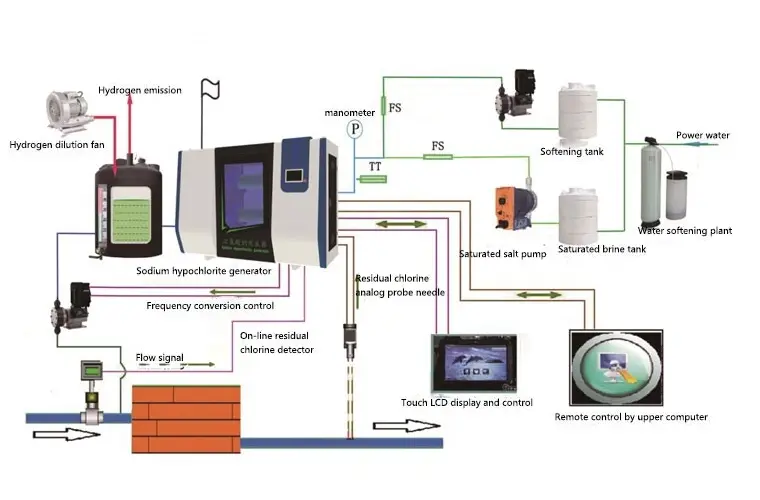
Sodium hypochlorite generator use in water plant
Why are water plants using sodium hypochlorite generators?
Water is an indispensable substance in people's lives, and a large amount of water resources are used every day. The water sources used by residents in their daily lives come from various water plants in the city. In order to ensure the safety of water use for residents, water plants will undergo a series of treatments, including disinfection of water quality. This is also a very important step in ensuring drinking water safety, Many water plants now choose to use sodium hypochlorite generators and have achieved very good results. So why are water plants using sodium hypochlorite generators?
Sodium hypochlorite generators are currently widely used in industries such as tap water disinfection, circulating cooling water treatment, swimming pool disinfection, and various types of wastewater treatment. As a generating device, the sodium hypochlorite generator not only meets the sterilization and disinfection needs of water plants, but also effectively controls the operating costs of water plants.
The use of sodium hypochlorite for disinfection in waterworks can be achieved through rapid reaction with water, where hypochlorite can combine with hydrogen ions in water to form hypochlorite, which then adsorbs on the surface of bacteria or viruses. Through internal action, it can change the internal structure of cells or viruses, thereby causing damage to bacteria or viruses, changing their characteristics, and achieving good sterilization and disinfection effects.
Solution
Reaction process of sodium hypochlorite generator
Chemical reaction equation
Anodic reaction: 2Nacl → 2Na++Cl+2e-
Cathodic reaction: 2H2O+2e - → H2 ↑+2OH-
Extreme reaction:2NaOH+Cl2→NaCLO+NaCL+H2O
Total reaction:Nacl+H2O→NaCLO+H2 ↑
Product parameter
Effective chlorine production: 50-400000g/H
Effective chlorine concentration: 3-10g/L
Installed power: 0.3-90KW
Host size: customized
Delivery cycle: 25 days
WhatsApp:+86 15806625431
Email: info@sdshinemachinery.com
Water plant applications
When used as a disinfectant for water supply, the amount of chlorine added afterwards can generally be around 2mg/l of effective chlorine,
while the amount of chlorine added before and after depends on the characteristics of the raw water. It is best to conduct small-scale experiments
on the amount of chlorine added before and after. If there is ammonia nitrogen in the water, a breakpoint chlorination effect will occur, and
small-scale experiments should be conducted for addition.
There can be multiple points for adding sodium hypochlorite, usually located in distribution wells, drop wells for effluent, and specialized mixing wells for
disinfection, which are conducive to the mixing of sodium hypochlorite. The contact time should not be less than 30 minutes. However, some factories
set the point for adding sodium hypochlorite at the inlet of the filter, believing that quantitative addition can facilitate the backwashing of the filter sand.
Personally, I do not recommend it because the addition of sodium hypochlorite will damage the biological effect of the filter sand and weaken the filtration
effect of the filter sand, And it also affects the measurement calculation of subsequent dosing.
When used as a disinfectant for sewage, the dosage is generally 3-7 times that of tap water disinfection, and the actual dosage should also be guided by
small-scale experiments; The dosing point is generally set at the total outlet point, such as the outlet of deep bed filters, biological filters, or the outlet of
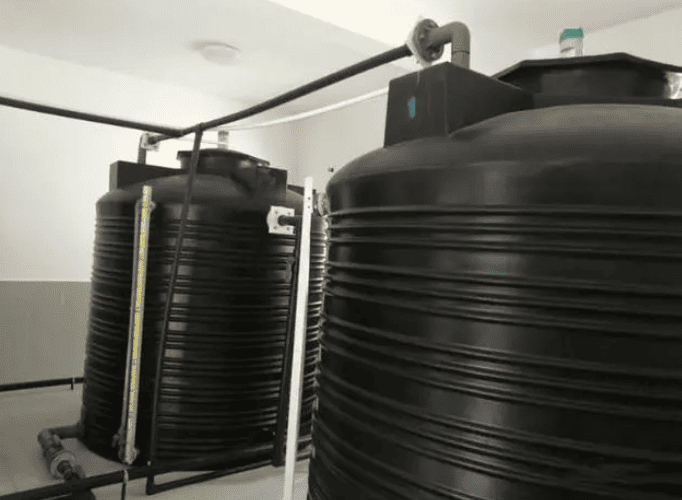
secondary sedimentation tanks. A dedicated clean water tank is also set up to accommodate the disinfected water. At present, secondary sodium
disinfection is mostly used in water plants with deep treatment, while water plants without deep treatment are less used due to lower discharge standards.
The main factors that affect the disinfection effect include pH, water temperature, contact time, turbidity, and chlorine dosage. The chlorine dosage is easy to
understand, and the larger the dosage, the better the disinfection effect. However, the characteristics and by-products of the effluent need to be considered in
the water supply, so the dosage should not be too large. Turbidity is also easy to understand. The more impurities in the water, the greater the amount of
chlorine consumed. Therefore, the reason why the dosing point is generally placed after filtration is because of this. The pH mainly affects the amount of
hypochlorous acid generated after the hydrolysis of sodium hypochlorite. Generally, the higher the pH, the worse the effect, and it should not exceed 7.5.
The water temperature is mainly reflected in the impact on the loss of residual chlorine. The higher the water temperature, the faster the loss of residual
chlorine. However, the higher the water temperature, the better the disinfection effect. This generally does not require special adjustment, and the normal
temperature in most areas is sufficient.
Chlorine disinfectants, due to their strong oxidizing properties, almost all have a coagulation aid effect, which is more commonly used in water supply and
less commonly used in wastewater. Algae containing raw water is a common type of raw water in China. Algae themselves and their metabolites carry
negative charges and are not easily removed by coagulation. At the same time, they can also chelate with metal ions in the water and penetrate the filter,
affecting the effluent quality. Moreover, algae have strong adsorption power and can adhere to the surface of the filter, affecting the filtration effect and
shortening the filter life. Chlorination has inhibitory and eliminating effects on algae, thereby improving the later coagulation effect.
Precautions for adding sodium hypochlorite generator to water plant
Generally speaking, the higher the concentration of sub sodium, the faster the attenuation. According to some of the author's own research, there are two
main culprits for the attenuation of finished sub sodium. One is ultraviolet radiation, and the other is temperature. Generally, under shading room temperature
conditions, 10% of finished sub sodium decays to 5% for about 120 days, and then the attenuation rate suddenly slows down. Therefore, many articles believe
that diluting to 5% for storage is acceptable. In fact, diluting 10% of sub sodium requires soft water, In many regions, the hardness of tap water is above 100,
and a large amount of scale will form when diluted. Water softening requires equipment, so it is generally recommended to store 10% finished sodium for
about 7 days before use. Another benefit of using it in the short term is that it can reduce the production of chlorate and chlorite. Sodium hypochlorite is
corrosive and easily decomposable, so it is best to use materials that are light shielded and corrosion-resistant for storage. PE drums are a good choice,
and when using PE drums, a gas outlet channel can be left to prevent gas accumulation.
Qualification certificate
Factory Display

Business negotiation